Windows Generate Ssh Key As Jenkins User
14.12.2020 admin
-->
Apr 01, 2020 Setup slaves from Jenkins master. F ollow the first 3 steps we did for slave configuration using username and password. Follow all the configuration in the 4th step. But this time, for the launch method, select the credential you created with the ssh key. May 10, 2018 Next step in adding SSH credentials on Jenkins requires us to have the private ssh key for the server we want to connect with Jenkins server. So let’s take a scenario, we want to connect to a server from jenkins with user ‘Dan’. To generate an SSH key in Windows 10: Ensure the Windows 10 OpenSSH client is installed. Run “ssh-keygen” in Command Prompt and follow the instructions to generate your key. Jul 22, 2019 After the copy of ssh-id to Slave machine Try logging into the slave machine by executing following command in Jenkins master machine ssh ‘jenkins@’. Setup of Credentials on Jenkins. On Jenkins dashboard click on the Credentials. Click on Global. Click on Add Credentials. Kind: SSH Username with private Key. Username: Jenkins. Private Key: Enter directly and paste the. First, you can generate an ssh key from any account. That account just has to be able to access the Jenkins user%USERPROFILE%.ssh folder. Ssh-keygen -t rsa -P ' -f C:USersJenkins Account.sshidrsa Second, use JENKINS SSH Credentials Plugin in order to register your private key, and register the public key to the GitHub repo you monitor.
This quickstart shows how to install Jenkins on an Ubuntu Linux VM with the tools and plug-ins configured to work with Azure. When you're finished, you have a Jenkins server running in Azure building a sample Java app from GitHub.
Prerequisites
- An Azure subscription
- Access to SSH on your computer's command line (such as the Bash shell or PuTTY)
If you don't have an Azure subscription, create a free account before you begin.
Create the Jenkins VM from the solution template
Jenkins supports a model where the Jenkins server delegates work to one or more agents to allow a single Jenkins installation to host a large number of projects or to provide different environments needed for builds or tests. The steps in this section guide you through installing and configuring a Jenkins server on Azure.
In your browser, open the Azure Marketplace image for Jenkins.
Select GET IT NOW.
After reviewing the pricing details and terms information, select Continue.
Select Create to configure the Jenkins server in the Azure portal.
In the Basics tab, specify the following values:
Name - Enter
Jenkins.User name - Enter the user name to use when signing in to the virtual machine on which Jenkins is running. The user name must meet specific requirements.
Authentication type - Select SSH public key.
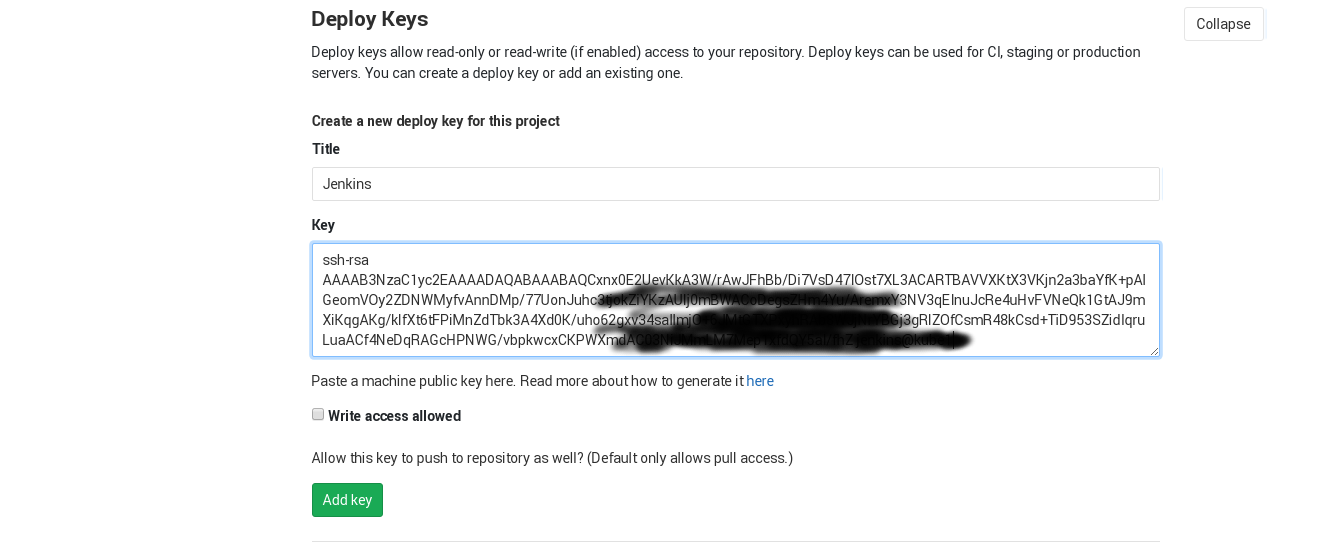
SSH public key - Copy and paste an RSA public key in single-line format (starting with
ssh-rsa) or multi-line PEM format. You can generate SSH keys using ssh-keygen on Linux and macOS, or PuTTYGen on Windows. For more information about SSH keys and Azure, see the article, How to Use SSH keys with Windows on Azure.Subscription - Select the Azure subscription into which you want to install Jenkins.
Resource group - Select Create new, and enter a name for the resource group that serves as a logical container for the collection of resources that make up your Jenkins installation.
Location - Select East US.
Select OK to proceed to the Additional Settings tab.
In the Additional Settings tab, specify the following values:
Size - Select the appropriate sizing option for your Jenkins virtual machine.
VM disk type - Specify either HDD (hard-disk drive) or SSD (solid-state drive) to indicate which storage disk type is allowed for the Jenkins virtual machine.
Virtual network - (Optional) Select Virtual network to modify the default settings.
Subnets - Select Subnets, verify the information, and select OK.
Public IP address - The IP address name defaults to the Jenkins name you specified in the previous page with a suffix of -IP. You can select the option to change that default.
Domain name label - Specify the value for the fully qualified URL to the Jenkins virtual machine.
Jenkins release type - Select the desired release type from the options:
LTS,Weekly build, orAzure Verified. TheLTSandWeekly buildoptions are explained in the article, Jenkins LTS Release Line. TheAzure Verifiedoption refers to a Jenkins LTS version that has been verified to run on Azure.JDK Type - JDK to be installed. Default is Zulu tested, certified builds of OpenJDK.
Select OK to proceed to the Integration Settings tab.
In the Integration Settings tab, specify the following values:
- Service Principal - The service principal is added into Jenkins as a credential for authentication with Azure.
Automeans that the principal will be created by MSI (Managed Service Identity).Manualmeans that the principal should be created by you.- Application ID and Secret - If you select the
Manualoption for the Service Principal option, you'll need to specify theApplication IDandSecretfor your service principal. When creating a service principal, note that the default role is Contributor, which is sufficient for working with Azure resources.
- Application ID and Secret - If you select the
- Enable Cloud Agents - Specify the default cloud template for agents where
ACIrefers to Azure Container Instance, andVMrefers to virtual machines. You can also specifyNoif you don't wish to enable a cloud agent.
- Service Principal - The service principal is added into Jenkins as a credential for authentication with Azure.
Select OK to proceed to the Summary tab.
When the Summary tab displays, the information entered is validated. Once you see the Validation passed message (at the top of the tab), select OK. Windows 7 ultimate activation key generator 2018.
When the Create tab displays, select Create to create the Jenkins virtual machine. When your server is ready, a notification displays in the Azure portal.

Connect to Jenkins

Navigate to your virtual machine (for example, http://jenkins2517454.eastus.cloudapp.azure.com/) in your web browser. The Jenkins console is inaccessible through unsecured HTTP so instructions are provided on the page to access the Jenkins console securely from your computer using an SSH tunnel.
Set up the tunnel using the ssh command on the page from the command line, replacing username with the name of the virtual machine admin user chosen earlier when setting up the virtual machine from the solution template.
After you have started the tunnel, navigate to http://localhost:8080/ on your local machine.
Get the initial password by running the following command in the command line while connected through SSH to the Jenkins VM.
Unlock the Jenkins dashboard for the first time using this initial password.
Select Install suggested plugins on the next page and then create a Jenkins admin user used to access the Jenkins dashboard.
The Jenkins server is now ready to build code.
Create your first job
Select Create new jobs from the Jenkins console, then name it mySampleApp and select Freestyle project, then select OK.
Select the Source Code Management tab, enable Git, and enter the following URL in Repository URL field: https://github.com/spring-guides/gs-spring-boot.git
Select the Build tab, then select Add build step, Invoke Gradle script. Select Use Gradle Wrapper, then enter complete in Wrapper location and build for Tasks.
Select Advanced and then enter complete in the Root Build script field. Select Save.
Build the code
Select Build Now to compile the code and package the sample app. When your build completes, select the Workspace link for the project.
Navigate to complete/build/libs and ensure the gs-spring-boot-0.1.0.jar is there to verify that your build was successful. Your Jenkins server is now ready to build your own projects in Azure.
Troubleshooting the Jenkins solution template
If you encounter any bugs with the Jenkins solution template, file an issue in the Jenkins GitHub repo.
Next Steps
How to generate an SSH key in Windows 10
Windows Generate Ssh Key As Jenkins User Manual
To generate an SSH key in Windows 10:
- Ensure the Windows 10 OpenSSH client is installed.
- Run “ssh-keygen” in Command Prompt and follow the instructions to generate your key.
Applies to Windows 10 1803, and up
Generating SSH keys in a Windows environment used to be a convoluted process which required the installation of third-party tools. Since the Windows 10 April 2018 update, Windows has shipped with a preinstalled OpenSSH client, which means you can use ssh-keygen to generate SSH keys. Read on as we walk you through the entire process.
First, you’ll need to make sure OpenSSH is installed on your machine – if you upgraded from an earlier version of Windows 10, you may need to manually enable it. Launch the Settings app and click the “Apps” category. Next, click the “Manage optional features” link. If you don’t see “OpenSSH Client” in the list which appears, click the “Add a feature” button and install it. You might need to reboot your PC after the installation.
Once OpenSSH is installed, you’re ready to proceed. Open Command Prompt from the Start menu. Type “ssh-keygen” (without the quotes) into the terminal window and press enter. You’ll be prompted to confirm the save location. We recommend pressing enter to use the default location in your user directory. Otherwise, type a path to save the key in and then press enter.
You can now choose to add a passphrase (password) to the key. If you add one, you’ll need to supply it whenever you use the key. Either type a passphrase and press enter or press enter immediately to proceed without one.
Windows will now generate your RSA public/private key pair. The public key will be stored as “id_rsa.pub” in the directory you specified. Upload this key to any machines you need to SSH into. You can then open a connection using Windows’ built-in SSH client – type “ssh [email protected]” to connect and authenticate using your generated credentials.